The map reveals stunning geological features on Mars in three dimensions.
A new map of Mars shows the Red Planet in stunning detail, revealing a wealth of fascinating geological features as seen from orbit.
The high-resolution map could help scientists answer a number of pressing questions about Mars including how it came to be a dry, arid, and barren landscape despite once being abundant with liquid water.
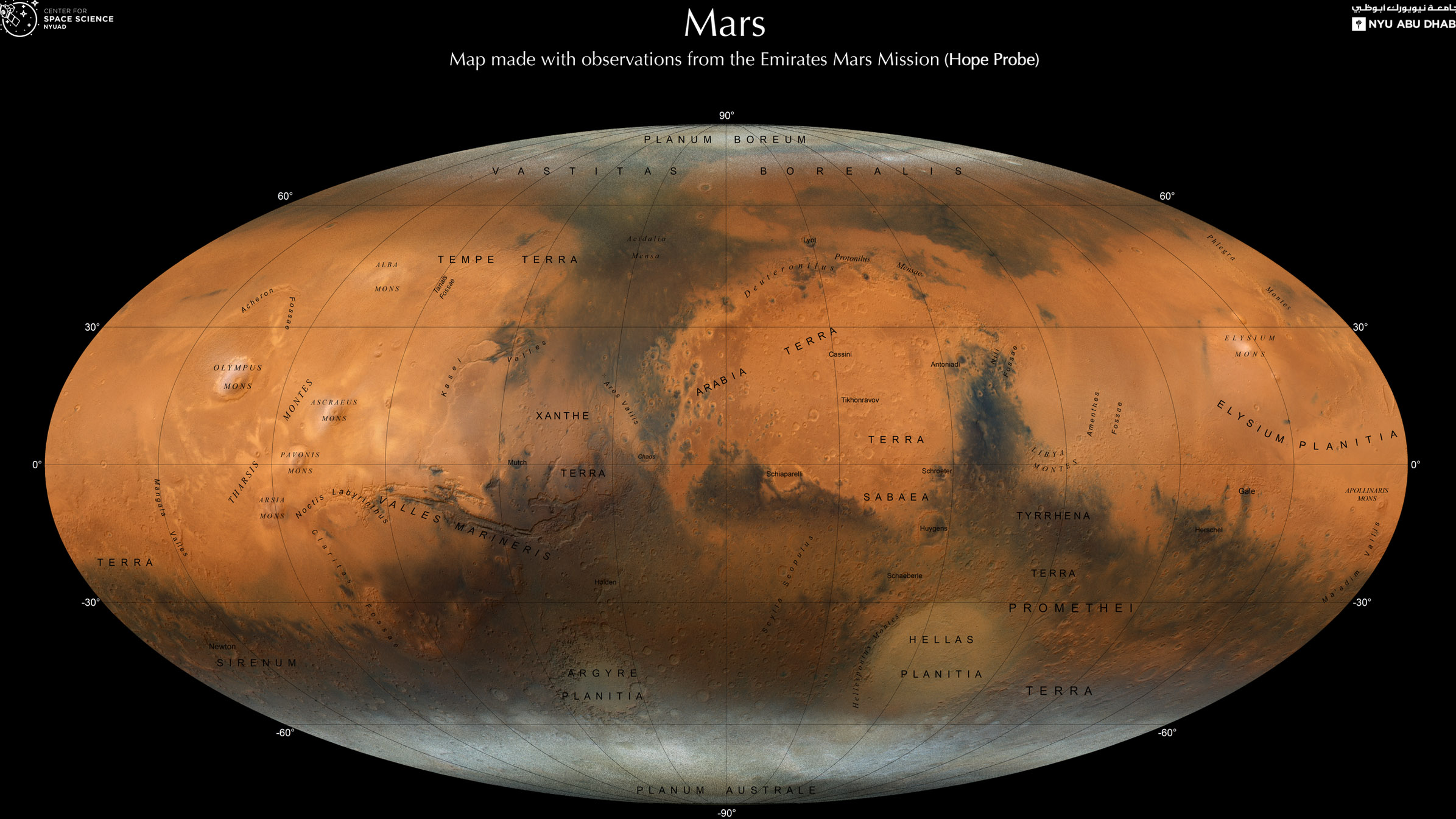
The Martian map was created by a team of scientists led by New York University Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) Center for Space Science(opens in new tab). The researchers used data collected from orbit around Mars by the Emirates Mars Mission (EMM), also known as Hope or Al-Amal.
The map shows the Red Planet through the eyes of Hope’s state-of-the-art onboard imaging system, the Emirates Exploration Imager (EXI), and is a testament to the growing influence of the UAE in science. In a statement, NYUAD wrote(opens in new tab) that it hopes the new Mars map will motivate young people in the UAE to pursue careers in STEM disciplines.

“We plan to make our map available to the entire planet, as part of the new and more advanced Atlas of Mars, which we have been working on, and will be available in both English and Arabic once published,” NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) group leader and research scientist Dimitra Atri said in the statement. “The hope is that this accessibility will make it a great tool for researchers, and also students to learn more about Mars, and showcase the possibilities that the space sector in the UAE can offer.”
To create the map, Atri and the team took over 3,000 observations from EXI taken over one Mars year,a period equivalent to two years here on Earth, and stitched them together to build a color composite. The resultant map shows many of the major geological features of the Red Planet in high resolution.

The map shows relics of ancient rivers, lakes, and valleys that were inundated with liquid water roughly 3.5 billion years ago, as well as mountains, long-inactive volcanoes, and polar ice caps. As a result, the image may aid planetary scientists in understanding how Mars’ temperature changed over billions of years to form the dry and desolate planet we see today.
According to Atri, “the complete Mars map also brings the UAE and the Arab world another step closer to achieving EMM’s ambitious mission goal to provide a complete global picture of the Martian climate.” “While EMM will track the seasonal changes over the course of a Martian year, more than 30 earlier spacecraft have only been able to take a snapshot of the weather on Mars.”
By allowing scientists to study the distribution of impact craters across the planet’s arid surface, the map also reveals the history of early asteroid bombardment of Mars. As such the composite of EXI images could also help researchers better understand the conditions in the tumultuous early solar system when space rock impacts were far more common than today.
The Hope orbiter is the first interplanetary mission from the UAE and from the Arab world as a whole. Commissioned by UAE leaders in 2014, the spacecraft was launched from Japan on July 20, 2020. After a journey of around seven months, Hope reached orbit around Mars on February 9, 2021.
“The Hope probe is helping researchers to create this global image of the planet due to its strategic position,” Atri said. “Hope circles Mars in an elliptical orbit that allows it to observe from much further away than any other spacecraft. This strategic position is helping researchers to create a global image of the planet.
The UAE’s and the entire Arab world’s first interplanetary mission is the Hope orbiter. The spacecraft was ordered by UAE leaders in 2014 and launched from Japan on July 20, 2020. On February 9, 2021, Hope arrived in orbit around Mars after a roughly seven-month voyage.
Because of its advantageous location, the Hope probe is assisting scientists in developing this comprehensive map of the planet, according to Atri. Hope travels around Mars in an elliptical orbit, which enables it to view from a great distance away from other spacecraft. This advantageous location is assisting researchers in constructing a comprehensive picture of the globe.







