The 3,000-year-old remains of an ancient fortification have been discovered at the bottom of Turkey’s largest lake. The underwater excavations were led by Van Yüzüncü Yıl University and the governorship of Turkey’s eastern Bitlis Province.

The castle is said to belong to the Iron Age Armenian civilization also known as the Kingdom of Van, Urartu, Ararat and Armenia. The lake itself is believed to have been formed by a crater caused by a volcanic eruption of Mount Nemrut near the province of Van. The current water level of the reservoir is about 150 meters higher than it was during the Iron Age.
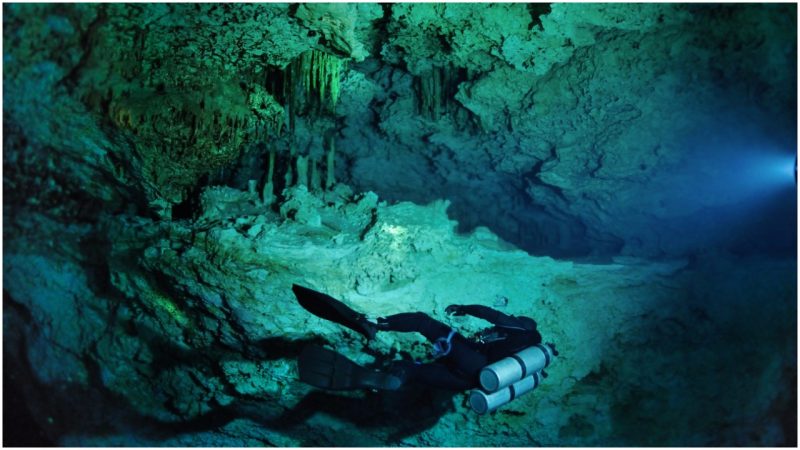


Divers exploring Lake Van discovered the incredibly well-preserved wall of a castle, thought to have been built by the Urartu civilization. Experts had been studying the body of water for a decade before it revealed the fortress lost deep below its surface.

The 3,000-year-old remains of an ancient fortification have been discovered at the bottom of Turkey’s largest lake. Divers exploring Lake Van discovered the incredibly well-preserved wall of a castle, thought to have been built by the Urartu civilization

Map of historic Armenian with Lake Van at its center.
Src: archaeology-world.com