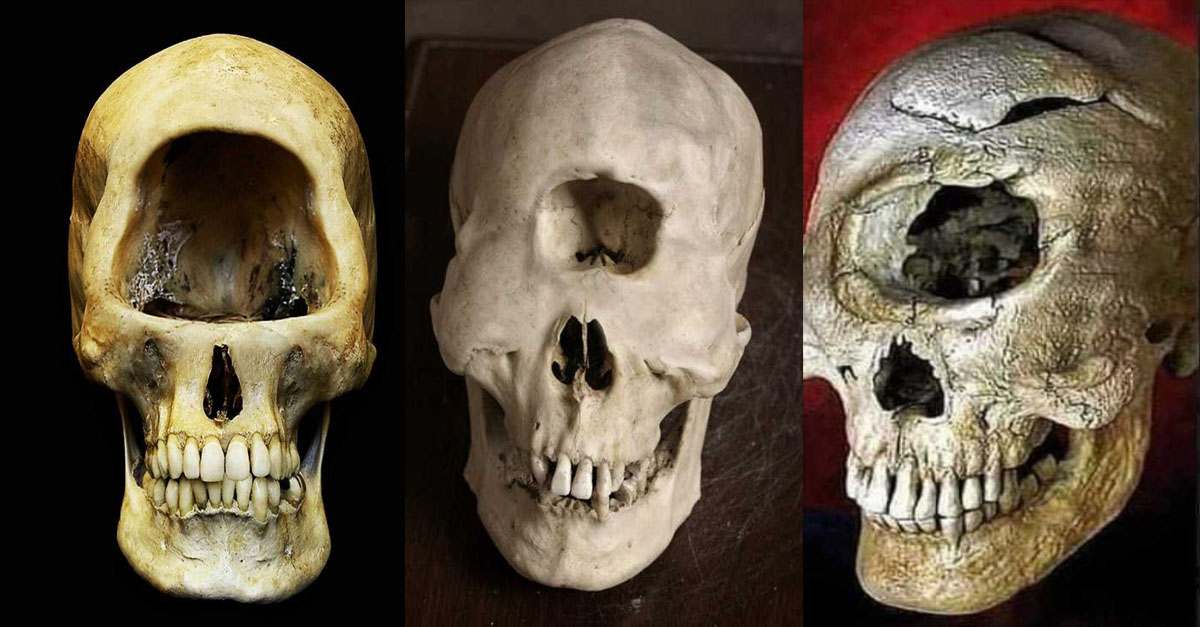
A new species of armored dinosaur has been identified from bones discovered more than two decades ago in Australia.
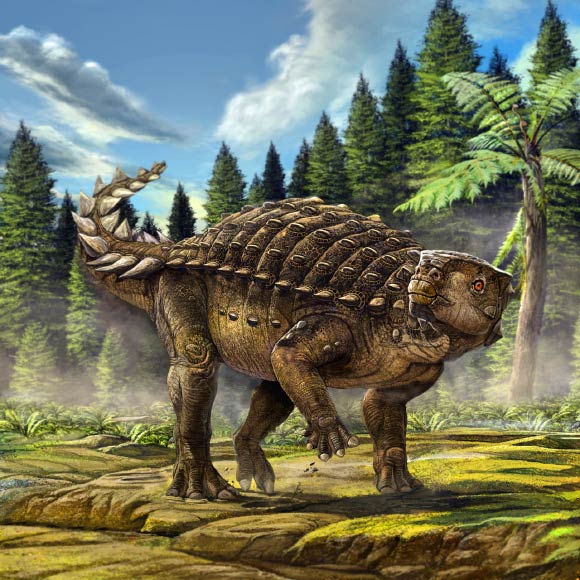

An artist impression of Kunbarrasaurus ieversi. Image credit: © Australian Geographic.
This new species is one of a group of four-legged armored herbivorous dinosaurs called ankylosaurs.
The near-complete skeleton of the 100 million-year-old (Cretaceous period) beast, including most of the skull and mandible, along with postcranial material, was discovered in 1989 in the Allaru Mudstone on Marathon Station near Richmond, north-western Queensland, by Mr Ian Ievers.
But new research led by University of Queensland paleontologist Lucy Leahey has revealed the specimen is a distinctly different species than previously thought.
“When it was first studied back in the 1990s, the fossil was placed it in the same genus as Australia’s only other named ankylosaur, Minmi, which is based on some bones from Roma in south-western Queensland,” Ms Leahey explained.
The find is one of the best-preserved ankylosaur fossils in the world and the most complete dinosaur so far discovered in Australia.
Ms Leahey and her colleagues named the new ankylosaur Kunbarrasaurus ieversi, a reference to the man who first found it.
“The species name honors Mr Ian Ievers, discoverer of the holotype. The name therefore means Ievers’ shield-lizard,” they explained.
“The generic name combines Kunbarra [kunbara], the Mayi (Wunumara) word for ‘shield’, and souros, the Greek word for ‘lizard’, and is a reference to the animal’s heavily ossified skin.”
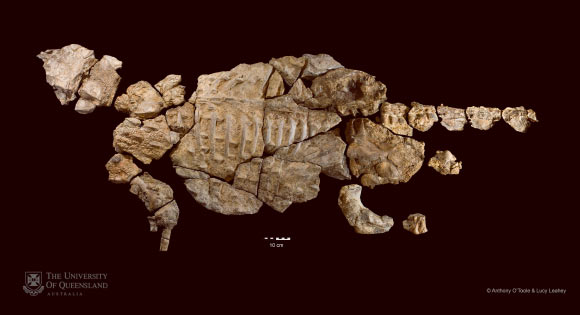
Kunbarrasaurus ieversi skeleton. Image credit: Anthony O’Toole / Lucy Leahey.
According to the team, Kunbarrasaurus ieversi had a parrot-like beak, bones in its skin and an inner ear similar to a turtle.
“Our work has also revealed that Kunbarrasaurus is more primitive than the majority of other well-known ankylosaurs from North America and Asia,” said team member Dr Steve Salisbury, also of the University of Queensland.
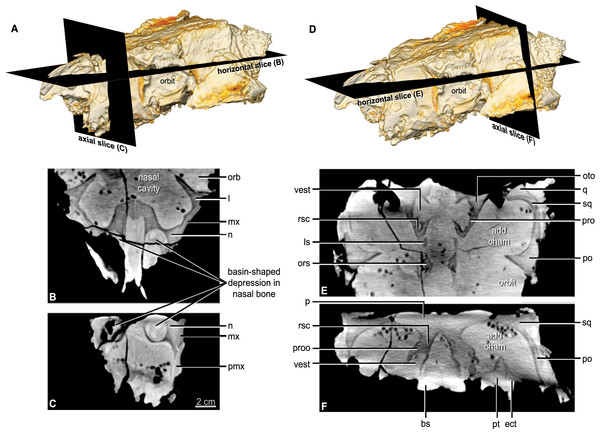
“It appears to represent an early, less heavily armored member of the group, close to the point at which the ankylosaurs diverged from the other main lineage of armored dinosaurs, the stegosaurs.”
Source: sci.news